Transport pipes - 9.0
|
Part Number |
Description |
|
2094-00006 |
100m reel PTFE tubing |
|
2094-01030 |
acrylic tubing |
Data for both the flexible PTFE and solid acrylic tubing is shown below.
Engineering specifications
|
Property |
PTFE |
Acrylic (PMMA) |
|
Inner diameter (mm) |
10 |
10 |
|
Outer diameter (mm) |
12 |
15 |
Mechanical properties
|
Property |
PTFE |
Acrylic (PMMA) |
|
Young's modulus (MPa) |
410 - 750 |
3200 |
|
Elongation (%) |
350-550 |
4 |
|
Compressive strength (MPa) |
7-8 |
103 |
|
Bending strength (MPa) |
5-6 |
107 |
|
Impact strength (J/cm) |
1.6 - 1.6 |
10 |
Physical properties
|
Property |
PTFE |
Acrylic (PMMA) |
|
Thermal expansion (e-6/K) |
100 - 100 |
78 |
|
Thermal conductivity (W/mK) |
0.23 - 0.25 |
0.19 |
|
Specific heat (J/kg.K) |
1000 - 1000 |
1470 |
|
Melting temperature (°C) |
327 - 327 |
160 |
|
Glass temperature (°C) 127 105-110 |
127 |
105-110 |
|
Density (kg/m3) |
2150 - 2200 |
1190 |
|
Resistivity (Ω.mm2/m) |
1e+22 |
1e+22 |
|
Friction coefficient |
0.05 - 0.08 |
0.45 – 0.8 |
|
Refraction index |
1.35 - 1.35 |
1.49 |
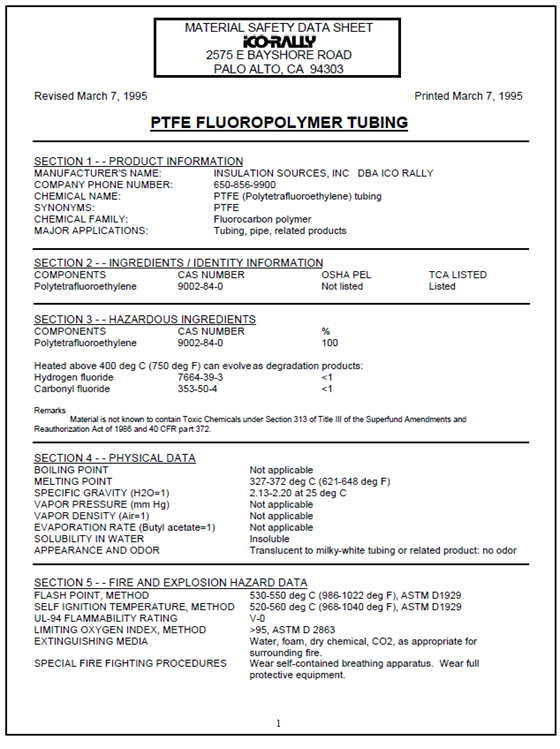
As the PTFE pipes are installed in conduits or trunking within the ceiling space, their MSDS is reproduced below, to assist you in complying with your local fire safety regulations.
PTFE Thin Wall Tubing Properties
| Material Properties | Data |
| Inside bending radius (mm) | 144 |
| Flexural modulus at room temperature (N/mm^2^) | 350 - 650 |
| Breaking strain according to ASTM D 790 (N/mm^2^) | 0.7 |
|
Burst pressure at 23°C (MPa) Note: pressure resistance at 50°C will be 50% of the pressure resistance at 23°C |
2.0 |
| Service pressure (estimated as 1/3 of the burst pressure) (MPa) | 0.7 |
| Tolerance on inside diameter (mm) | 0.3 |
| Tolerance on excentration (for 2mm wall thickness) | 0.2 |
| Stability and reactivity | Data |
| Stability | Stable at normal temperatures and storage conditions. |
| Resistance to atmospheric agents and light | Test pieces of PTFE, exposed for over twenty years to the most disparate climatic conditions, have not shown any alteration of their characteristic properties. |
| Resistance of PTFE to chemical agents | PTFE is practically inert against known elements and compounds. It is attacked only by the alkaline metals in the elementary state, by chlorine trifluoride and by elementary fluorine at high temperatures and pressures. |
| Solvent resistance | PTFE is insoluble in almost all solvents at temperatures up to about 300°C. Fluorinated hydrocarbons cause a certain swelling which is however reversible; some highly fluorinated oils, at temperatures over 300°C, exercise a certain dissolving effect upon PTFE. |
| Regulatory Information | Data |
| Components | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| CAS Number | 9002-84-0 |
| OSHA PEL | Not listed |
| TCA Listed | Listed |
| Ingredients with occupational exposure limits to be monitored | None |
| UL-94 Flammability Rating | V-0 |
| Hazardous ingredients | Data |
|
Material is not known to contain Toxic Chemicals under Section 313 of Title III of the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986 and 40 CFR part 372. Heated above 400°C (750°F) can evolve as degradation products: |
|
| Hydrogen fluoride \<1% | Ref. CAS 7664-39-3 |
| Carbonyl fluoride \<1% | Ref. CAS 353-50-4 |
| Health risks | Data |
| Toxicological information | Under normal conditions of use, no harmful effects on man are known. |
| Carcinogen | PTFE has no cancerogenic effect. |
| Inhalation |
Inhalation of fumes from overheating (above 300°C / 572°F) PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) may cause polymer fume fever, a temporary flu like illness with fever, chills, and sometimes cough, of approximately 24 hours duration. Trace amounts of carbonyl fluoride and hydrogen fluoride may also be evolved when PTFE is overheated or burned above 400°C (750°F). Inhalation of low concentrations of HYDROGEN FLUORIDE can initially include symptoms of choking, coughing, and severe eye, nose, and throat irritation. This is possibly followed after a symptomless period of one to two days by fever, chills, difficulty in breathing, cyanosis, and pulmonary edema. Acute or chronic overexposure to HF can injure the liver and kidneys. Inhalation, ingestion, or skin or eye contact with CARBONYL FLUORIDE may initially include: skin irritation with discomfort or rash; eye corrosion with corneal or conjectural ulceration; irritation of the upper respiratory passages; temporary lung irritation effect with cough, discomfort, difficulty in breathing, or shortness of breath. Individuals with pre-existing diseases of the lungs may have increased susceptibility to the toxicity of excessive exposures from thermal decomposition products. |
| Skin Contact | Does not irritate human skin |
| Eye Contact | May cause eye irritation |
| Personal protection | Data |
| Respiratory | Where the material temperature is above 300°C (572°F), use a positive pressure supplied air respirator. |
| Eye protection | Not normally required |
| Protective clothing | Not normally required |
| First aid measures | Data |
| Inhalation |
No specific intervention is indicated as the PTFE tubing is not likely to be hazardous by inhalation. Consult a physician if necessary. If exposed from fumes from overheating or combustion, move to fresh air. Consult a physician if symptoms persist. |
| Skin Contact | PTFE tubing is not likely to be hazardous by skin contact. |
| Eye Contact | In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with plenty of water and get medical attention if irritation occurs. |
| Fire and explosion hazards | Data |
| Risk |
If a flame is applied to the material it will ignite but if the flame is removed then combustion ceases. Limited flame spread and low smoke generation (NFPA 262-1990, UL-910). Complies with NFPA definition of “limited combustible” material. |
| Flash point | 530-550°C (986-1022°F), ASTM D1929 |
| Self ignition temperature | 520-560°C (968-1040°F), ASTM D1929 |
| Melting Point | 327/335°C |
| Explosion risk | No explosion risk |
| Suitable extinguishing media | Water, foam, CO~2~ and dry extinguishing media, as appropriate for surrounding materials |
| Firefighting |
Products will emit toxic fumes at high temperatures. Hazardous gases/vapors produced in a fire are hydrogen fluoride (HF), carbon monoxide, and potentially toxic fluorinated compounds. Approved pressure demand breathing apparatus and protective clothing should be used for all fires. Protect from hydrogen fluoride fumes which react with water to form hydrofluoric acid. Wear neoprene gloves when handling refuse from a fire involving PTFE |
| Environmental information | Data |
| The material does not harm the environment but is not biologically degradable. | |
| Transport | Not classified as hazardous under transport regulations. |
| Disposal | No specific risks. The product must be disposed in accordance with the local authorities. Recycling is suggested. |


Transport pipes - 9.1 Installing PTFE pipes >>>
.png?width=300&height=157&name=spt%20logo%20png%20(1).png)